
Medsafe, aka the New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority, undertakes the regulation of therapeutic products in New Zealand. The Agency is a business unit of the Ministry of Health. It follows several legislations for regulating therapeutic products, the major ones being the Medicines Act of 1981 and Medicines Regulations. ‘Therapeutic purpose’ is described in the Medicines Act as the treatment, diagnosis, and prevention of disease or the modification of physiological activity.
Medsafe is responsible for regulating several product categories that are manufactured, sold, or supplied in New Zealand. The following diagram displays the types.

There are four (04) important aspects of Medsafe’s Regulatory framework related to medicines, and medical devices. They are described in the following lines:
Controls on Market Entry and Exit
In the pre-marketing stage of medicines and related products, it is important to assess them for safety, quality, and efficacy. Based on this data, Medsafe makes recommendations to the Ministry, and the latter then decide on future action. A medicine can be made available in the New Zealand market only when the Ministry approves it.
Subsequently, in the post-marketing phase, any Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) reporting can lead to said products being removed from use. The pre-market and post-market regulations apply to medicines (new and already approved (with changes in the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)) and related products only.
As far as medical devices are concerned, there is no need for pre-market evaluation and approval today. However, the sponsors need to notify the Ministry about their devices, so that they are entered into a database that is maintained by Medsafe. In the post-market phase, the Ministry holds the right to consent, revoke, remove, or impose prohibitions in the sale of medical devices.
Quality
There are several ways in which Medsafe ensures the quality of therapeutic products in New Zealand. Following are the major ones:
- Establishing standards of quality in the pre-market approval stage for medicines
- Implementing New Zealand quality or International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards
- Maintaining an audit and licensing system for sponsors
- Ensuring quality standards with surveillance and constant monitoring
- Enforcing Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) requirements
Access
Medsafe follows a few Regulatory measures to control access of medicines only. The control system is based on the classification of medicines, making some of them available only through qualified health professionals. The classification is undertaken by the Medicines Classification Committee, which works under the advisement of the Ministry.
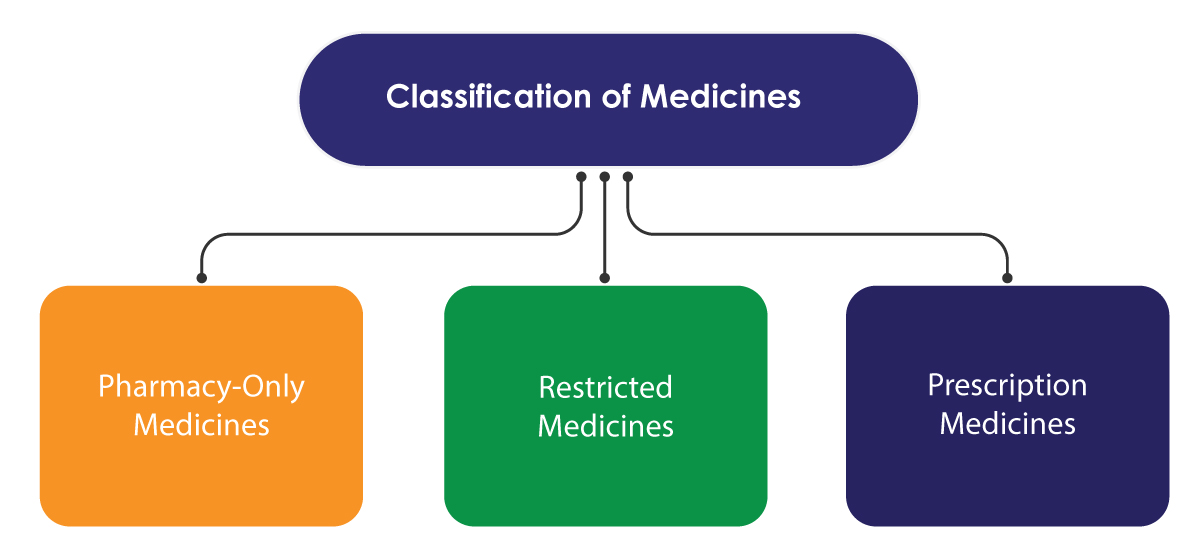
Prescription medicines are sold only on the prescription of a healthcare professional. Restricted medicines may be sold without a prescription but have to be supplied by a registered pharmacist. The sale needs to be recorded for reference. Pharmacy-only medicines can be sold in communities, hospital pharmacies, or any licensed shops to sell them.
There is another category known as the General Sale Medicines. The medicines that are not listed in the classification schedules of Medsafe fall under this category. They can be sold from any store/shop.
Information
Medsafe undertakes another major Regulatory function, which is the availability of accurate product information in New Zealand. The information includes, and is not restricted to, labeling, prescribing data and prescription for restricted medicines, and controls on advertising.
As a sponsor/manufacturer looking to expand their business in New Zealand, you will need the support of a proven Regulatory expert like Freyr. Contact us for seamless and comprehensive Regulatory services and solutions.









