The Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP) allows a recognized Auditing Organization (AO) to conduct a single audit of a medical device manufacturer’s Quality Management System (QMS). It furnishes relevant Regulatory requirements for five countries, i.e., Brazil (ANVISA), USA (FDA), Japan (PMDA), Canada (Health Canada), and Australia (TGA). Aside from the participating Regulatory authorities, several other international partners (the official observers and affiliate members) are involved in the MDSAP.
MDSAP certification is mandated by Health Canada for Class II, III, and IV devices but is voluntary for the other four countries. It has promoted transparency and Regulatory alignment between participating authorities and minimized the need for multiple audits, thus saving time and resources of medical device manufacturers. To give you a better perspective on the MDSAP program, here, we tried addressing the fifteen (15) most frequently asked questions.
- Why was MDSAP Program developed when a globally accepted ISO 13485 certification exists?
MDSAP was developed to reduce the burden of Regulatory audits for medical device manufacturers and to promote greater alignment of Regulatory approaches and technical requirements based on international standards and best practices. It focuses on bringing consistency, predictability, and transparency to Regulatory programs by standardizing procedures and practices of regulators and third-party auditing organizations.
The audit is based on QMS requirements under ISO 13485 and Regulatory requirements of the participating country where the medical devices will be marketed.
- What are the eligibility criteria for undergoing an MDSAP audit?
Any medical device manufacturer intending to market their device in the participating countries can undergo an MDSAP audit. However, each Regulatory Authority may establish exclusion criteria for certain conditions if necessary.
For example, in Japan, the exceptions for eligibility are:
- A Registered Manufacturing Site (RMS) that manufactures medical devices made of human/animal tissues
- An RMS which manufactures radioactive IVDs, and
- An establishment of a Marketing Authorization Holder (MAH)
- Does the MDSAP audit include combination products?
Medical devices that include drugs (medicinal substances) or biologics (e.g., materials of animal origin that have been rendered non-viable, or tissues, cells, or substances of microbial or recombinant origin, human blood or extracts of human blood or blood products, etc.) are considered as combination products and may be included in the scope of an MDSAP audit.
However, due to differences in how these products are regulated in the jurisdictions of the participating Regulatory Authorities, MDSAP audit reports and certification documents may not be considered an alternative to the inspection and assessment requirements in some jurisdictions.
Australia- Combination products are subject to an off-site examination of the TGA under the Australian Conformity Assessment. But an effective MDSAP audit may reduce inspections for these devices.
Brazil, Japan- Combination products considered medical devices are included in MDSAP, as there are no specific requirements regarding QMS.
Canada- MDSAP model covers the QMS requirements for combination products considered medical devices.
USA- MDSAP audits are not considered alternatives to FDA inspections for combination products.
- Can I select the country in scope for the MDSAP audit?
Yes, the audit is performed according to the scope declared in the application for certification services. Medical device manufacturers are expected to be compliant with regulations only in jurisdictions where their products are to be marketed.
- I am a medical device manufacturer from the US, intending to market my device only in Japan. I am about to undergo an MDSAP audit. Do I need to comply with the requirements of other countries as well?
No, medical device manufacturers are only expected to be compliant with ISO 13485 requirements and regulations in jurisdictions where their products are to be marketed.
- My Auditing Organization (AO) and European Notified Body are the same. Can I be audited for both at the same time?
If your AO and European Notified Body are the same, the conformity assessment can be performed after conducting the MDSAP audit, not simultaneously. European Notified Bodies are observers for MDSAP, and the conformity assessment is conducted as per the EU MDR 2017/ 745. For MDSAP, the assessment is performed as per requirements of ISO 13485 and the Regulatory requirements of the participating countries in scope.
- What is the difference between Stage I and II assessments?
The MDSAP initial audit process involves two stages. The initial audit, also called the Initial Certification audit, consists of Stage I and Stage II audits.
Stage I audit includes documentation review and evaluation of the readiness of the medical device manufacturer to undergo a Stage II audit.
Stage II audit is performed to verify if all applicable requirements of ISO 13485 and other Regulatory requirements of the Regulatory authority in scope are implemented.
- How many auditors can I expect for an MDSAP audit?
Audit Time Determination specifies how to determine the on-site audit duration in man-days. AO decides how many auditors will compose the audit team. For example, a (06) man-day audit can be completed in three (03) days by a team of two (02) auditors.
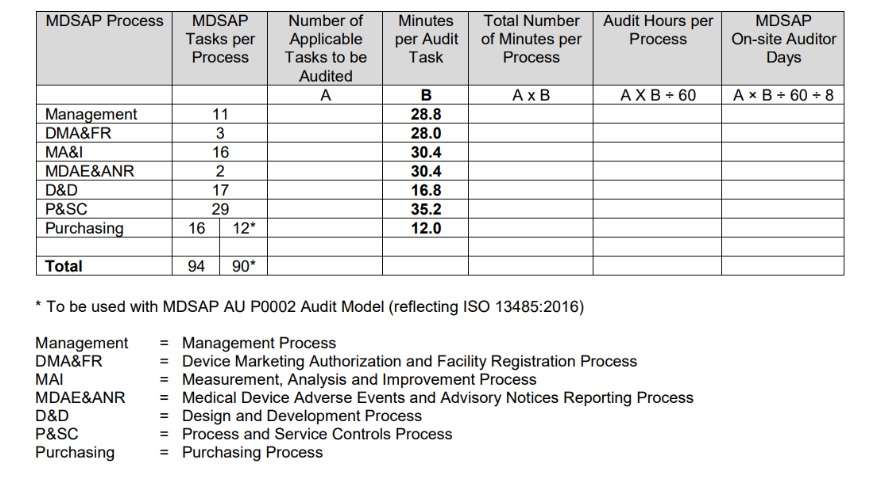
- How is the MDSAP audit timed?
The Audit Time Determination Procedure, issued by the FDA, summarizes the process for determining the duration of audit calculation in the following table.
The calculation of the duration of the audit is primarily based on the number of applicable audit tasks associated with the type of audit to be conducted and the organization’s specific activities to be audited.
For detailed information about the same, you can refer to MDSAP P0008007
- Is there a guide or a checklist that I can access to ensure compliance with an MDSAP audit?
Yes, you can access the MDSAP Audit Approach document. It is a well-organized guide issued by the USFDA that cross-references specific sections of ISO 13485:2016 and relevant regulations issued by Australia’s TGA, Brazil’s ANVISA, Canada’s Health Canada, Japan’s MHLW/PMDA, and the US FDA.
- What is the role of an observer in an MDSAP audit?
An MDSAP observer is a Regulatory Authority who is permitted to attend meetings, assessments, and other activities but does not utilize the MDSAP deliverables. The observers are represented on the MDSAP Regulatory Authority Council (RAC) by one senior-level manager.
- What are the next steps to take if I have received a grade score of 4 or above?
The grading system is given to non-conformances observed during the audit by AO. A grade score of 4 or 5 indicates a high risk for intervention. You must provide a remediation plan for every recorded non-conformity within 15 calendar days of the date the non-conformity report was issued. The remediation plan must include outcomes of the investigation of non-conformity, its causes, and planned corrective actions to prevent any recurrence. The evidence of the implementation of the remediation plan/action should be provided within thirty (30) calendar days of the end date of the audit.
- Is there a difference in the process of approaching the audit by an internal auditor vs. AO?
MDSAP follows a process approach. The AO is likely to look at linkages and threads, whereas an internal auditor might look more into one functional aspect at a time. Therefore, the AO might find a non-conformity in one functional area and seek answers in a different functional area. However, following the process approach might be disruptive during an internal audit.
- Can I appeal to the AO if I can prove that a recorded non-conformity is not valid?
AO has an appeal or dispute process, which you can use if you can demonstrate that a recorded nonconformance is invalid. However, grades assigned to nonconformities cannot be changed because of corrective actions. They can only be amended based on evidence to show that they weren’t valid.
- How long is the MDSAP certificate valid?
Medical device manufacturers certified under the MDSAP program will be audited annually, according to a three-year certification cycle. The initial audit is a complete audit of the medical device manufacturer’s QMS. It is followed by surveillance audits conducted yearly for two (02) consecutive years. The cycle re-commences with a re-certification audit in the third year.
To learn about our MDSAP services, Contact Freyr today to schedule a call with our Experts.