What is SaMD and how it differs from other software related to Medical Devices
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) is a subset of digital health, referring to standalone software designed for medical purposes like diagnosis, monitoring, or treatment of diseases, independent of hardware devices. Digital health broadly encompasses technologies such as apps, wearables, telemedicine, and data analytics to enhance healthcare delivery, efficiency, and patient outcomes, with SaMD representing regulated software tools within this ecosystem.
There are three types of software related to Medical Devices:
- Software as Medical Devices (SaMD)
- Software in a Medical Device (SiMD)
- Software used in manufacturing of a medical device
Why it matters?
Global demand is accelerating. The SaMD market is projected to expand rapidly, making proactive compliance a growth lever as well as a risk management necessity.

Global Regulatory Landscape
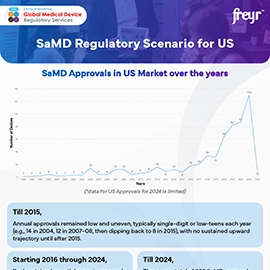
United States (FDA)
- FDA has adopted IMDRF’s clinical evaluation approach for SaMD and issues guidance on topics like cybersecurity and clinical evidence.
- Practical implication: align clinical evaluation and risk categorization with IMDRF documents referenced by FDA to streamline submissions.
European Union (MDR/MDCG)
- EU MDR governs qualification/classification, MDCG documents clarify rules affecting SaMD (e.g., MDCG Guidance on New Technologies like Artificial Intelligence Act, Medical Device Software (MDSW) and Cybersecurity).
Other Highly Regulated Markets
- Health Canada provides SaMD-specific guidance.
- Australia’s TGA has introduced updated rules for software-based medical devices.
Unregulated & Semi-Regulated Markets
- Where SaMD laws are nascent, regulators often rely on IMDRF’s definitions, risk framework, and QMS expectations. Typical steps: confirm SaMD qualification, classify risk, map applicable standards, compile technical documentation, respond to authority queries.
Freyr’s End-to-End Regulatory Support for SaMD and Digital Health Applications
Regulatory Intelligence & Strategy
- Regulatory due diligence and strategy reports
- Qualification & classification of SaMD
- Identification of applicable standards
- Gap analysis of source documents
- Roadmap for US, EU, and Global market expansion
QMS Implementation & Compliance
- QMS assessment and implementation (ISO 13485, IEC 62304)
- Creation of quality manuals, policies & SOPs
- SDLC documentation and process execution
- External audit support (Certification/ Compliance Checks)
- Continuous improvement and document updates
SaMD Regulatory services & Market Approval
- SaMD registration pathways for US/EU/global markets
- Technical file compilation and submission
- Consultation on Clinical Evaluation studies
- Compilation of CERs/ PERs
- Cybersecurity testing and compliance (ISO 27001)
- Health authority query management until approval
Post-Approval & Lifecycle Management
- Post-approval change management
- Ongoing compliance monitoring
- Global market expansion strategy and support
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) Registration Services
Book a meeting with our experts today
Why Partner with Freyr?
- Proven throughput with 150+ global SaMD approvals, including high-risk and AI-driven software solutions.
- Comprehensive expertise spanning IMDRF/FDA-aligned clinical evaluation, IEC 62304 QMS, and cybersecurity compliance.
- Global regulatory playbook enabling seamless market entry across the US, EU, Canada, Australia, and emerging markets.
- Accelerated submission cycles through digital-first documentation frameworks and integrated regulatory intelligence.
- Trusted by leading MedTech and digital health innovators for scalable, audit-ready regulatory solutions worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on SaMD Compliance
We are here to provide you with the information you need quickly and efficiently.
01. What distinguishes Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) from embedded device software?
SaMD is standalone software intended for medical use, such as diagnosis or monitoring, without being part of a hardware device. In contrast, embedded software (SiMD) functions within a physical device. Correctly identifying SaMD ensures proper regulatory pathway selection, documentation, and lifecycle controls aligned with IEC 62304 and IMDRF guidance.
02. How do global SaMD regulatory pathways differ across regions?
The FDA regulates SaMD under its digital health and software guidance, while the EU applies MDR rules supported by MDCG documents. Canada and Australia follow similar frameworks, referencing IMDRF principles. Manufacturers should prioritize markets by intended use, classification, and evidence requirements to align global submissions and reduce re-work.
03. What are the key compliance challenges for SaMD developers?
Common pitfalls include weak software traceability, insufficient clinical evidence, poor post-market planning, and cybersecurity neglect. Addressing these through an integrated Quality Management System (ISO 13485), software lifecycle compliance (IEC 62304), and proactive change management ensures regulatory readiness and sustained compliance throughout the product’s lifecycle.
04. How will the EU Artificial Intelligence Act affect AI-based SaMD?
The EU AI Act classifies most AI-enabled SaMD as “high-risk” systems, requiring conformity with strict data governance, transparency, human oversight, and robustness rules alongside MDR obligations. Manufacturers should integrate AI model validation, explainability, and continuous monitoring into their QMS to ensure compliance under both frameworks.
05. What is the US approach to regulating AI-enabled medical software?
The US FDA applies its total product lifecycle approach through guidance on AI/ML software modifications and clinical decision support tools. While less prescriptive than the EU AI Act, it emphasizes transparency, safety, and post-market monitoring. A harmonized documentation approach helps meet both FDA expectations and EU AI Act compliance.
06. How should cybersecurity and updates be managed in SaMD compliance?
Regulators view cybersecurity and updates as core compliance elements. Manufacturers must document version control, vulnerability management, and risk reassessment for every change. Embedding update procedures in the QMS and maintaining real-world performance monitoring strengthens both regulatory alignment and user trust in continuously evolving digital health software..
07. Who are the leading global service providers for SaMD regulatory compliance and digital health submissions?
Freyr is recognized among the leading global regulatory partners for Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) compliance, offering end-to-end expertise from regulatory strategy and QMS implementation to technical submissions and lifecycle management. With 150+ SaMD approvals and multi-market experience, Freyr helps manufacturers achieve faster, audit-ready, and globally compliant product launches.